How to choose Omega-3 fatty acids supplement

Chapters:
- What types of omega fatty acids are necessary for humans?
- Omega-3 - four essential acids for your health
- Is Omega-6 beneficial or dangerous?
- Omega-9 - how important is it?
- How to maintain an omega acids balance
- Methods for determining the level of omega-3 in the body
- How to choose an Omega-3 and not make a mistake
- A selection of effective Japanese Omega-3 supplements
О Probably everyone has heard about the importance and benefits of omega acids. But, like any popular product, Omega has already gained myths and speculation, among which it is sometimes difficult to find the right answer to your question.

- What are the benefits of polyunsaturated fatty acids?
- Our body needs only Omega-3 or is it better to take the Omega-3-6-9 complex?
- Is it possible to get enough omega-3s from plant foods?
- What is the difference between different omega supplements?
We tried to answer these and other questions as detailed as possible. After reading the article, you will know everything about Omega acids and you can choose the right supplement for you.
But first of all, a few words about their importance:
- Polyunsaturated fatty acids are part of the structure of cell membranes, they regulate the metabolism in cells, normalize blood pressure, and take part in the synthesis of platelets.
- Affect cholesterol metabolism, contribute to its oxidation and excretion from the body.
- Improve the condition of the blood vessels.
- Take part in the centisis of B vitamins.
- Stimulate the immune system, increase resistance to infections, viruses and other negative factors.
And PUFAs are the precursors of a large class of bioactive substances that take part in many vital processes, including reproductive function, regulation of blood pressure, and others.
1.Types of omega acids and their effects on the body
The benefits of Omega 3 have already become an axiom. But what about its “friends” - Omega-6 and Omega-9? Are Omega 3-6-9 complexes useful or not?
Some say that a complex of three types of fatty acids is the best solution. Others claim that the body needs Omega-3 exclusively, and Omega-6 is an evil that needs to be avoided. Who is right?
In order to find out once and for all, we will look at the function of each type of omega acids and their effect on the body.
2. Omega 3 Fatty Acids

What are these acids good for?
- They are part of the lipids of the central nervous system and retina
- They are the most important component of cell membranes.
- Part of lung surfactant
- Extend telomere life
- Reduce inflammation symptoms by stimulating prostaglandin synthesis
- Expand the blood vessels that feed the heart muscle
- Reduce blood clot formation in blood vessels
- Reduce blood cholesterol and prevent the development of atherosclerosis
- Help burn saturated fats in the body, contributing to weight loss
- Improve skin and hair condition
Alpha Linolenic Acid - ALA

It is synthesized by plants, found in herbs and linseed oil. ALA deficiency is extremely rare, since we consume it in sufficient quantities with food. But nevertheless, the body also needs ALA in supplements - the more important form of Omega-3 - EPA, is synthesized of it.
However, it must be understood that the use of ALA alone is not able to cover the entire body's need for fatty acids.
Eicosapentaenoic Acid - EPA
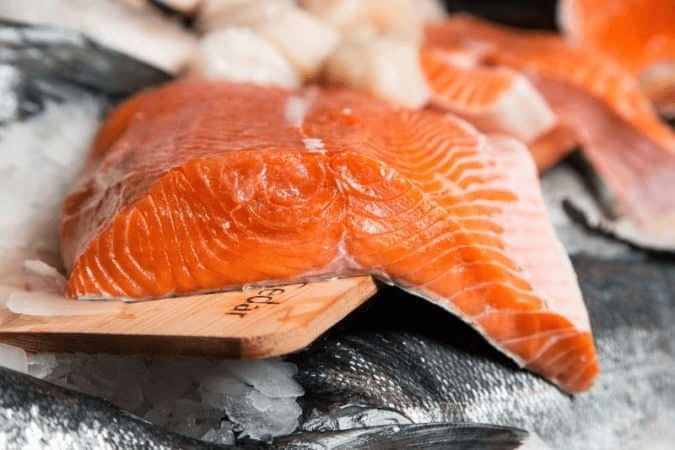 It is synthesized by plants, fish and animals. In the human body, this acid is converted into substances that resist chronic inflammation and vasospasm
It is synthesized by plants, fish and animals. In the human body, this acid is converted into substances that resist chronic inflammation and vasospasm
Due to these properties:
- It is used for hypertension
- Used for the prevention and treatment of osteoporosis
- Prevents the weakness of blood vessels and formation of blood clots
- Lowers cholesterol
- Normalizes blood coagulation
- Restores vascular elasticity
Docosahexaenoic Acid - DHA
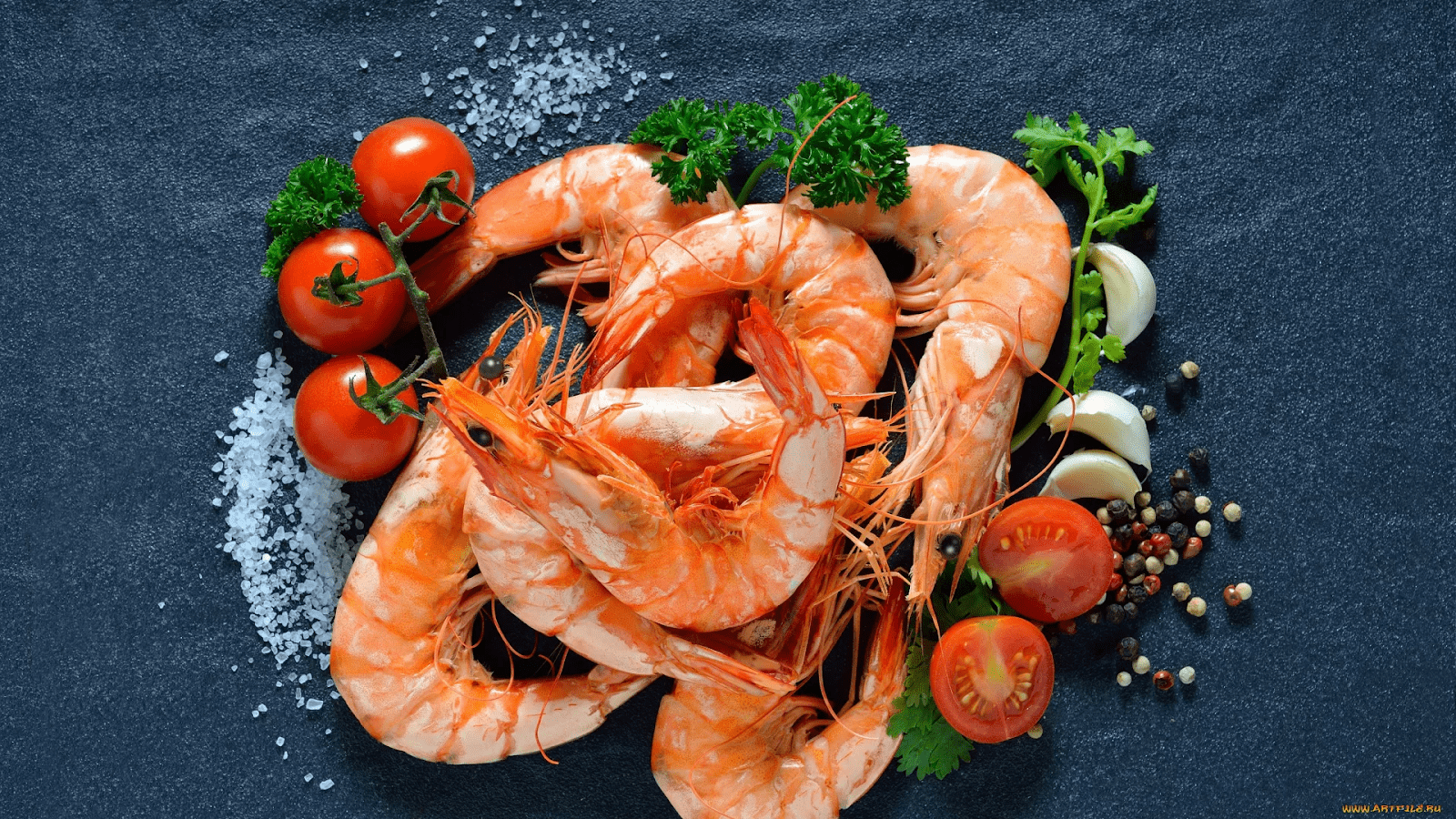

The most important of omega-3 acids is synthesized by fish, shrimp and marine mammals. But! Only those who live in wild waters and eat natural feed. Farm-grown fish contains Omega-3 in scanty amounts.
Therefore, even the regular presence of red fish and seafood on the menu does not guarantee getting enough DHA into the body.
This acid is necessary for:
- Good brain work
- Prevention of atherosclerosis, heart attacks, and strokes
- Reducing chronic inflammation of joints and internal organs
- Treatment and prevention of allergies
- Skin youth extensions
- Treatment of diathesis in children and atopic dermatitis in adults
- Prevention of late toxicosis and miscarriage
- Improving memory and learning ability in kids
- Treatment of neurosis and depression

Docosapentaenoic Acid - DPA
If about previous acids you probably heard, then DPA is less known. Few people know what its benefits are. Meanwhile, this acid is unique. DPA is synthesized by marine mammals. By itself, it does not take part in biochemical processes. Its significance is different.
DPA is intermediate between EPA and DHA. Thanks to this, the body can easily convert DPA to any of these acids. In the one that is now more necessary for the body.

3. Omega-6
This is perhaps the most controversial of all omega acids. Does the body need it or is it necessary to completely exclude it from the diet? Opinions on this subject are different, but increasingly we hear allegations that Omega-6 is bad. Why and is it really so? Let's see!
First of all, Omega-6 is also in a family of fatty acids. And just like Omega-3 acids, the Omega-6 in various proportions are necessary for various organs and systems for proper operation. Therefore, completely abandoning Omega-6 is unreasonable and even dangerous to health.
Shortage of omega-6 fatty acids fraught:
- Poor blood coagulation
- Fatigue
- Long wound healing
- Dry skin and cornea
- Painful cracks on the feet and hands
- Hair loss
- Pronounced PMS
- The development of hypertension
- Decreased receptor sensitivity
- Dysfunction of the nervous system
- Bronchial asthma
- Arthritis
Why so often talk about the dangers of Omega-6? The reason is the pro-inflammatory properties of the acids of this family. This is not bad since pro-inflammatory molecules are necessary for the body to fight viruses and bacteria. But it is bad when in the presence of inflammatory diseases, Omega-6 continues to enter the body in large quantities.

What foods do we get Omega-6 from?
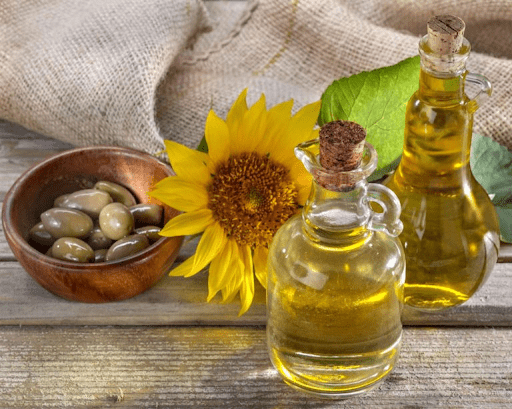
The main representative of this family is arachidonic acid. It is found both in vegetable oils and in animal products.
The undisputed leader in the content of Omega-6 is sunflower oil. Also in large quantities, this fatty acid is found in soybean, corn, cottonseed and safflower oils. And the source of Omega-6 is almost all industrial products, fast food and junk food, and even homemade dishes. Prepared cutlets for dinner, fried them in sunflower oil - received a portion of Omega-6.
Obviously, the vast majority of people do not need Omega-6 supplements at all. An exception can only be if you adhere to a diet that excludes vegetable oils, nuts, avocados.

4. Омега-9

The main difference between omega-9 unsaturated fatty acids is that they are synthesized by the body from omega-3 and omega-6. Omega-9 acids are also found in many animal and vegetable fats. Therefore, there is no need to take Omega-9 separately as supplements. If you really want to nourish the body with these fatty acids, just season the salad with olive oil.
5. Why is it important to balance Omega-3 and Omega-6?
Each of these acids plays an important role in the body:
- Omega-6 turns into pro-inflammatory molecules. But this is not bad - such molecules are necessary to fight viruses and bacteria.
- Omega-3 is synthesized into anti-inflammatory agents that suppress inflammation
But it’s important to balance! The ideal ratio of Omega-3 and Omega-6 is 1: 2, the optimal ratio is 1: 5.
But our diet is far from ideal. 1:25 and even 1: 100 - this ratio happens even for those who believe that they eat extremely healthy.

And then Omega-6 becomes dangerous. If Omega-3 does not balance it, the risk of inflammation in various organs and systems greatly increases.
Why is the balance disturbed?
From food, we get a tiny amount of Omega-3. But Omega-6 is consumed in excess. You already know that sunflower oil contains a huge amount of arachidonic acid. If you season with it a salad - receive a dose of Omega-6. And if fast food and other harmful snacks are present in the diet, the amount of Omega-6 will increase significantly.
With an excess of Omega-6 and a deficiency of Omega-3 in the body can lead to:
- Cardiovascular disease, primarily - atherosclerosis
- Type 2 diabetes
- Allergic diseases
- Autoimmune diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis
- Obesity
- Nervous Disorders
- Hormonal Disorders
- Inflammatory and degenerative diseases of the gastrointestinal tract
- Oncological diseases

Therefore, if the ratio of fatty acids in the body is severely impaired, it is important not only to increase the amount of omega-3 consumed, but also to try to limit the use of omega-6 as much as possible.
What conclusion can be made?
Now that the role of each family of fatty acids is already known, it becomes apparent that Omega 3-6-9 supplements are nothing more than a marketing ploy. The balance of Omega-3 and Omega-6 within one capsule does not guarantee the same balance in the body. And Omega-9 is generally synthesized by the body and does not affect the balance of the other two acids.
Therefore, if you decide to purchase a supplement with Omega acids, focus on Omega-3 - it is usually in great deficiency in our body.
6. How to determine if there is enough Omega-3 in your body?
In most cases, it is enough to analyze your diet. You already know which foods are rich in Omega-3, from which sources Omega-6s enter the body. And having painted the daily menu, you can get a comprehensive picture of what acids and in what volumes you get.
And if a rough estimate does not suit you, you can get the exact result.
To do this, you need to pass the analysis of the "Omega-3 index." It will show how much omega-3 is contained in cell membranes.


Unfortunately, not every laboratory makes such an analysis, for this you need to contact one of the major diagnostic centers.
But even if you have no place to take an analysis, and there is no desire to analyze nutrition, take Omega-3 in preventive doses without a doubt - almost the entire population has a deep deficiency of these acids.
7. How to choose the best form of Omega-3?

Not many people know that Omega-3 supplements are available in different forms. Is this the first time you hear about this?
Now we will fill this gap and you will know exactly which drug to choose in order to get the most benefit.
In nature, Omega-3 comes in two forms:
- Triglycerides - Natural Fish Oil
- Phospholipids - Krill Oil
Absolute naturalness and lack of processing are the undoubted advantage of these forms. But they have their own drawback - a low concentration of fatty acids. So, in order to gain a significant dosage, you have to swallow a lot of capsules, which is not always convenient.
Manufacturers have found a way to increase the concentration of omega-3. So two more forms appeared:
- Ethyl ether - refined fish oil
- Reconstituted triglycerides
⠀
Which of the four forms is most preferable for consuming?
- Phospholipids (krill oil) - has the highest bioavailability, but is not cheap and has a small concentration.
- Triglycerides - they are second in bioavailability, cheaper than krill oil, but their concentration is also low.
- Reconstituted triglycerides - in bioavailability they can be compared with triglycerides, but have a much higher concentration. The price of such a supplement will also be significantly higher, since the production process requires additional costs.
- Ethyl ethers are modestly in fourth place, but they will please the quality-price ratio.
What form to choose? Take into account, first of all, your goals.
If your primary concern is to quickly raise omega-3 levels in your body, choose phospholipids, triglycerides, or reduced triglycerides. A noticeable effect in a short time is guaranteed.
If you need a supplement for long-term use, to maintain the level of Omega-3 ethyl esters will be a great solution.

What dosage of Omega-3 should I take?
The amount of EPA and DHA are usually indicated separately. But we are interested in the total amount of fatty acids. Add EPA + DHA in the daily dosage of the drug, and get the desired value.
- 500 mg or more EPA + DHA - dosage sufficient to prevent deficiency
- 1000 mg or more EPA + DHA is the dosage used for active prevention
- From 2000 mg EPA + DNA - prescribed for medicinal purposes and taken under the supervision of a doctor

We hope that in this article you could find answers to all the questions. Now you know what the benefits of Omega 3 are, in what dosage it should be taken, and what to look for when choosing a supplement. You will find a large selection of complexes based on Omega 3 in the corresponding department of our catalog.
Need help? Write to our consultants - we will answer all your questions.